Choosing a suitable crane safety monitoring system(Safe Load Indicator/Load Moment Indicator) requires comprehensive consideration of regulatory requirements, equipment types, functional needs, technical performance, and supplier services. Below is a detailed selection guide:
1. Ensure Regulatory and Standard Compliance

Local Regulations as Priority
- Mandatory requirements for crane safety monitoring systems vary by country/region. Ensure the system complies with local standards:
China: Must adhere to TSG 51—2023 Safety Technical Regulations for Lifting Machinery, etc.
United States: Must comply with OSHA standards (e.g., Clause 1910.179), etc.
European Union: Must pass CE certification and comply with Machinery Safety Directives (2006/42/EC) and harmonized standards (e.g., EN 13001 series), etc.
Industry-Specific Requirements
- Additional standards for explosion-proofing, corrosion resistance, etc., may apply in scenarios such as petrochemicals and ports.
Certification and Qualification Audit
- Verify that the supplier’s system has relevant certifications (e.g., China Special Equipment Inspection and Research Institute certification, EU CE certification) and request test reports.
2. Match Crane Types and Operational Scenarios
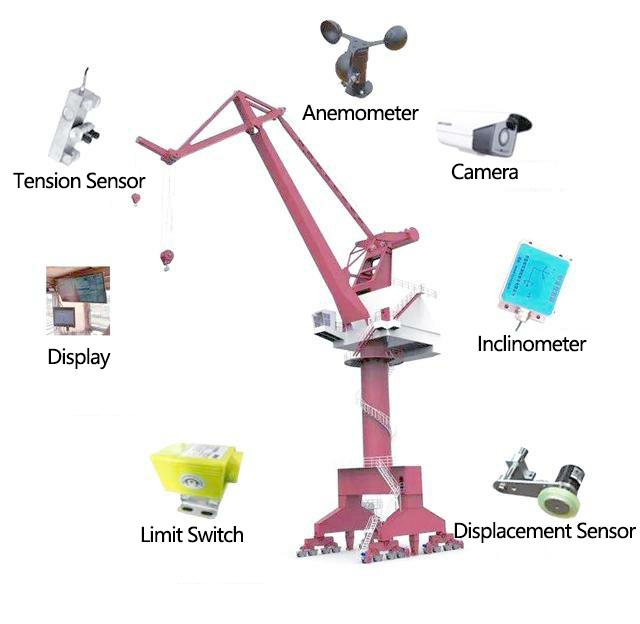
Function Selection Based on Crane Types
| Crane Type | Core Monitoring Parameters | Typical Scenarios |
| Tower Crane | Lifting capacity, load moment, amplitude, height, slewing angle, wind speed | Construction sites, high-rise building projects |
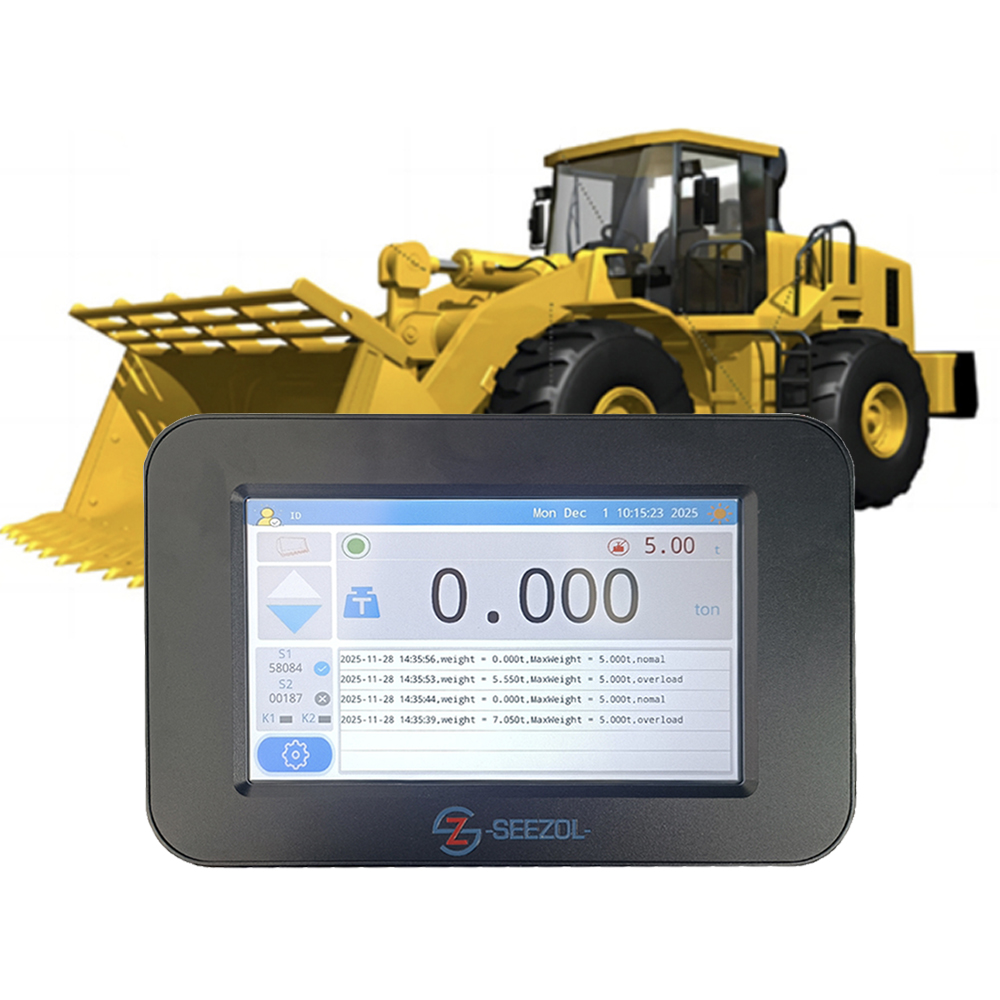
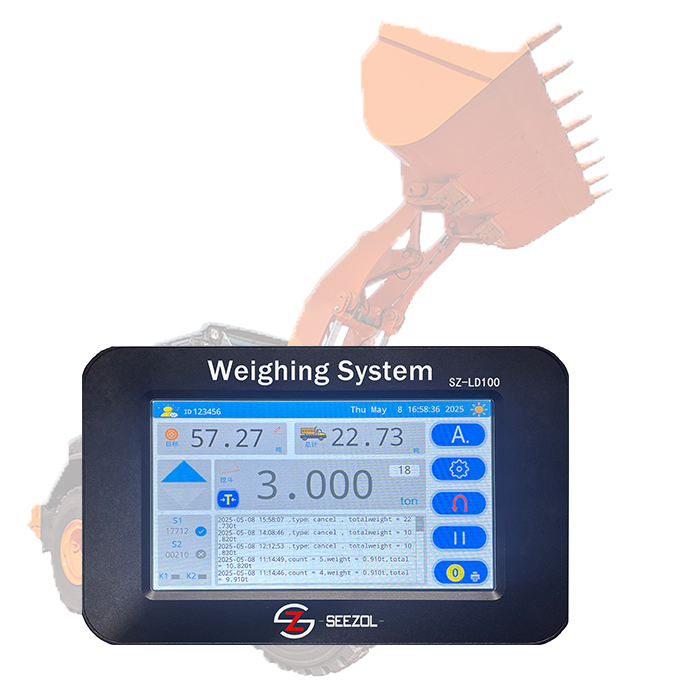
| Gantry Crane/Overhead Crane | Lifting capacity, load moment, travel distance, track deviation, collision prevention | Ports, factories, warehousing logistics |
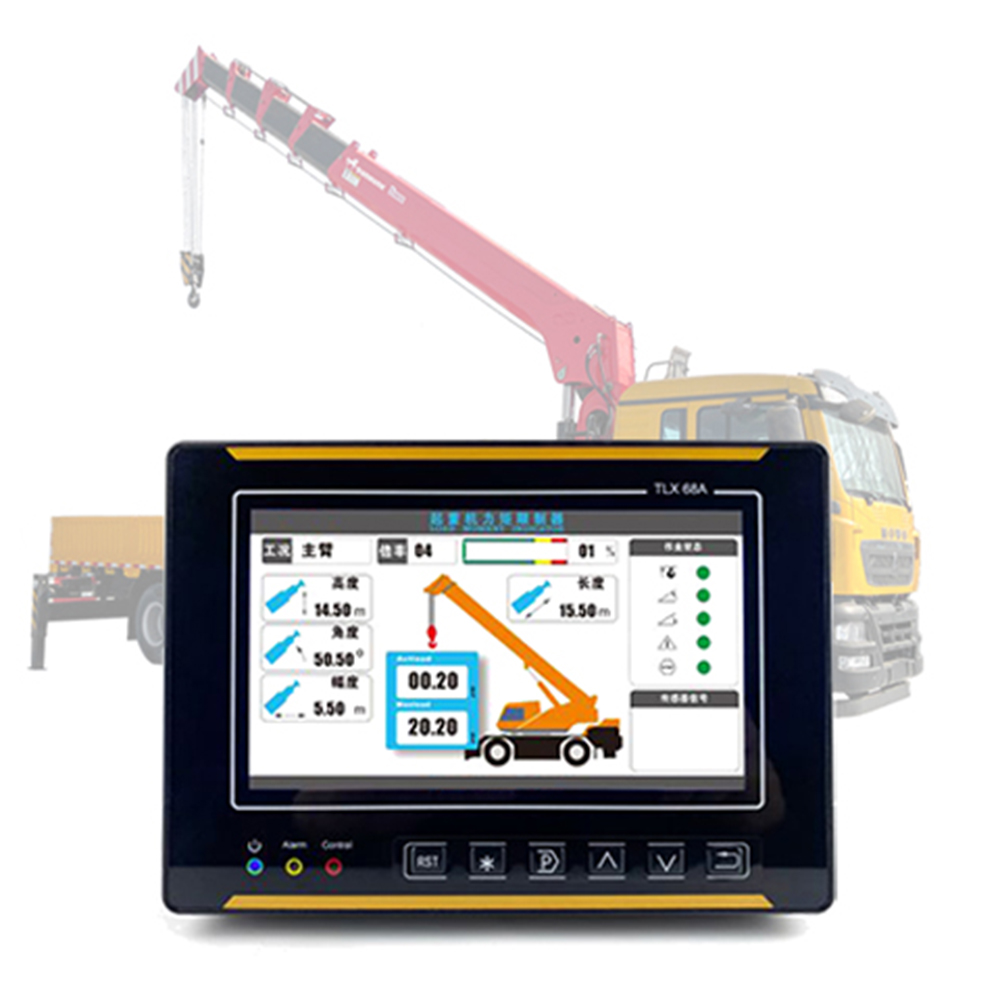
| Mobile Crane/Crawler Crane | Lifting capacity, load moment, inclination angle, outrigger pressure, ground bearing capacity | Outdoor hoisting, heavy equipment handling |
| Metallurgical/Explosion-Proof Crane | High-temperature adaptability, explosion-proof rating, real-time temperature monitoring | Steel plants, chemical workshops |
Environmental Adaptability
Harsh Working Conditions: Select industrial-grade sensors for high temperature, humidity, dust, and vibration environments.
Outdoor Operations: Consider water resistance, sun protection, and electromagnetic interference resistance.
Explosion-Proof Scenarios: Choose sensors and control systems with explosion-proof certifications (e.g., Ex certification).
3. Evaluate Core Functions and Technical Performance

Basic Monitoring Functions
Mandatory Functions: Lifting capacity limitation, load moment limitation, height/amplitude limit, travel monitoring, real-time data display, and alarms (audio-visual).
Optional Extended Functions:
Remote monitoring (transmit data to cloud platforms via 4G/5G, support mobile APP viewing);
Automatic control (e.g., power cutoff and intelligent collision prevention when thresholds are exceeded);
Data storage and analysis (historical data tracing, fault early warning models, maintenance cycle recommendations);
Personnel safety linkage (e.g., integration with personnel positioning systems to prevent unauthorized entry into hazardous areas).
Technical Performance Indicators
Accuracy: Lifting capacity monitoring error ≤ ±3%; angle/displacement monitoring error ≤ ±1°/±1mm (adjust according to operational conditions).
Response Speed: Alarm response time < 1 second; automatic control action time < 2 seconds.
Reliability: Mean time between failures (MTBF) ≥ 10,000 hours; sensor protection grade ≥ IP65.
Compatibility: Support integration with existing PLC and SCADA systems; open API interfaces for integration with enterprise management platforms.
Summary: Key Decision-Making Dimensions
| Dimension | Consideration Points |
| Regulatory Compliance | Local standard mandates, certification qualifications |
| Equipment Matching | Crane type, operational environment, monitoring parameter requirements |
| Technological Advancement | Accuracy, response speed, compatibility, scalability |
By following these steps, you can systematically select a crane safety monitoring system that meets safety requirements and business needs, minimizing operational risks and improving management efficiency.








